EC Controller Technical Solution
Design Innovation
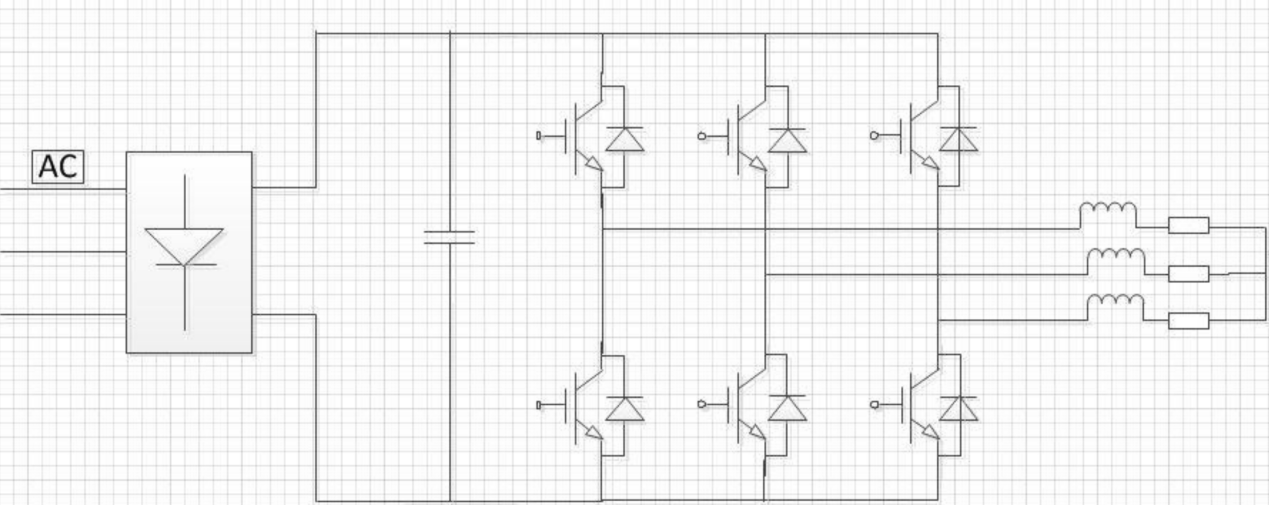
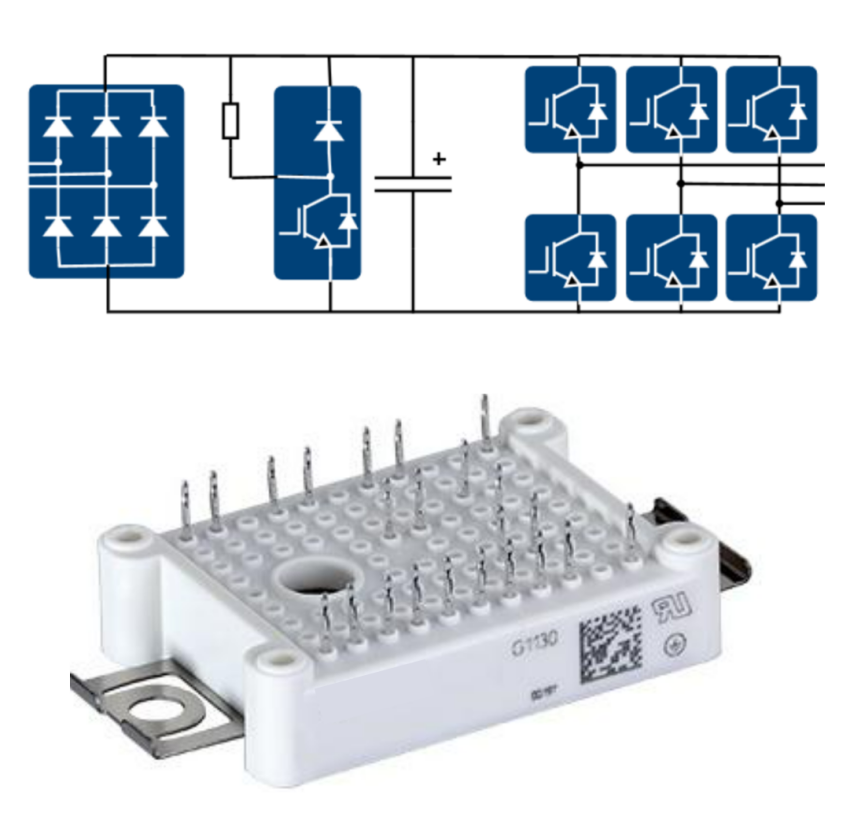
Integrated heat dissipation design
In high-power controller design, heat dissipation is a critical factor affecting reliability. The primary heat-generating components of the controller are rectifier diodes and inverter switches. Compared to traditional structures where rectifier modules and inverter modules are dissipated separately, this project's controller adopts an integrated rectifier+ inverter design, simplifying the heat dissipation structure and enhancing consistency and reliability in heat dissipation.
Electrolyte-free rectifier control system
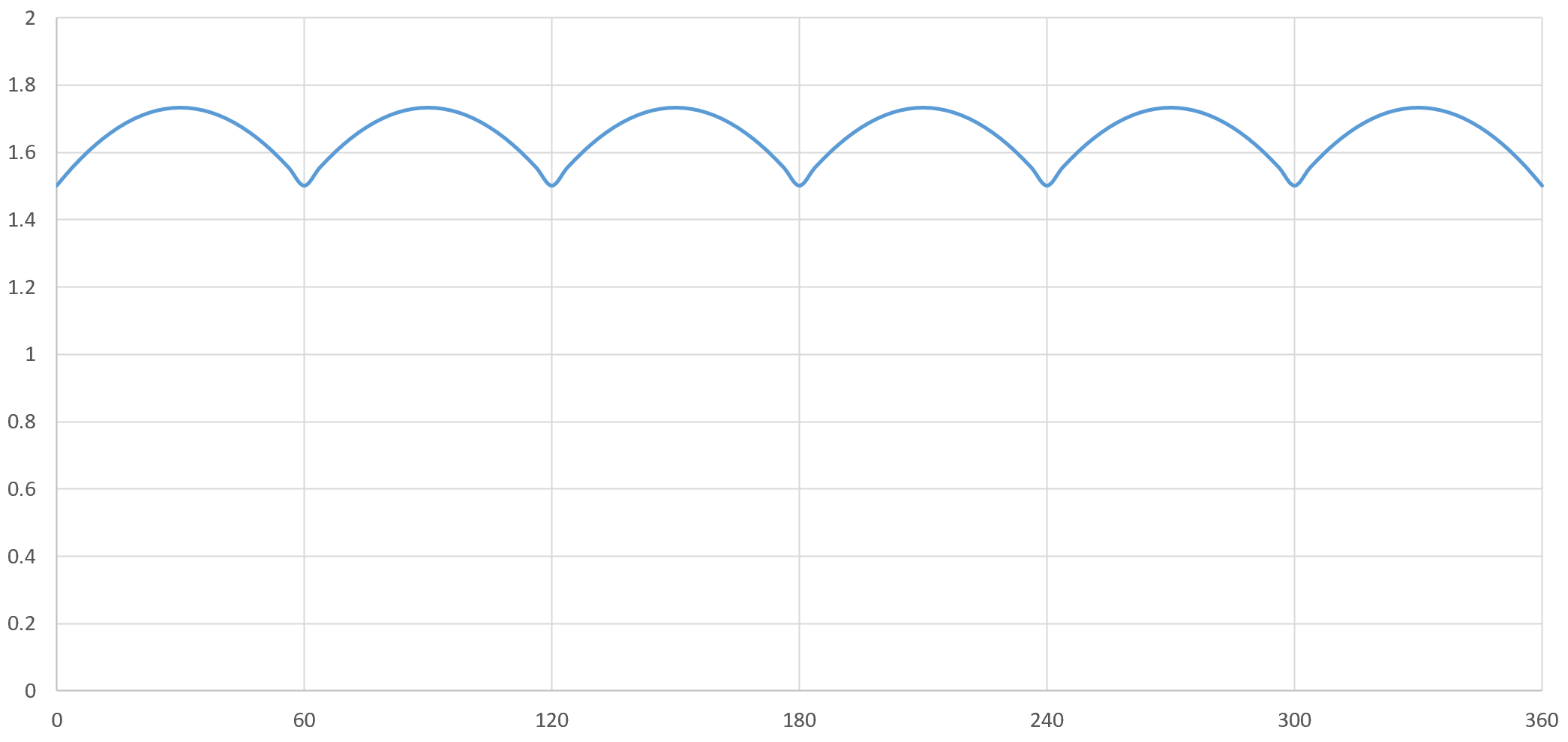
In traditional rectifier-inverter systems, a large-capacity electrolytic capacitor is typically added to maintain the stability of the bus voltage after rectification. For single-phase power input, this capacitor is generally essential. In systems powered by three-phase input, due to the additional two-phase input, the output voltage does not drop to zero even without a capacitor. Instead, it becomes a pulsating voltage at 6 times the input voltage frequency, with the lowest voltage approximately 0.86 times the maximum voltage.
Leveraging this characteristic, the control scheme of this project adopts a design scheme without rectifier filter electrolysis.
At the same time, due to the absence of large-capacity electrolytic capacitors, the bus voltage basically follows the output rectifier voltage, and the supply voltage and current can be directly output to the motor winding. Therefore, the power factor of the power supply part can reach more than 0.95, which greatly reduces the harmonic current of the power supply system and reduces the impact on the power grid.
